 Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
What Are You Looking For?
Anyone who has handled custom grades neodymium magnets may have noticed an unusual phenomenon: as the magnetic grade increases—from N35 all the way to N52—the physical strength of the magnet tends to decrease, rather than increase. Users are sometimes surprised to find that high-performance magnets break during assembly, crack when two magnets collide, and even break under moderate pressure. This is not a manufacturing defect, but rather stems from the fundamental science of magnetic properties at the microstructural level.
The Trade-off Between Strength and Structure
Neodymium magnets are produced through a sintering process, which involves compacting, arranging, and heating neodymium iron boron powder until a solid material is formed. To achieve higher magnetic grades, manufacturers must tune the internal microstructure to maximize remanence (Br) and coercivity (Hcj).
Achieving these properties requires:
These changes enhance magnetic output but also reduce mechanical toughness, making high-purity magnets more brittle.
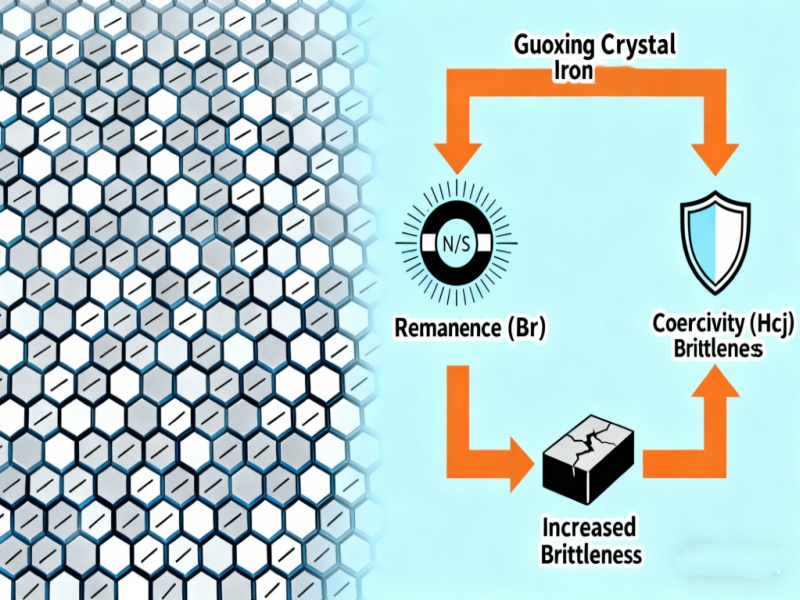
Why are high-purity magnets more brittle?
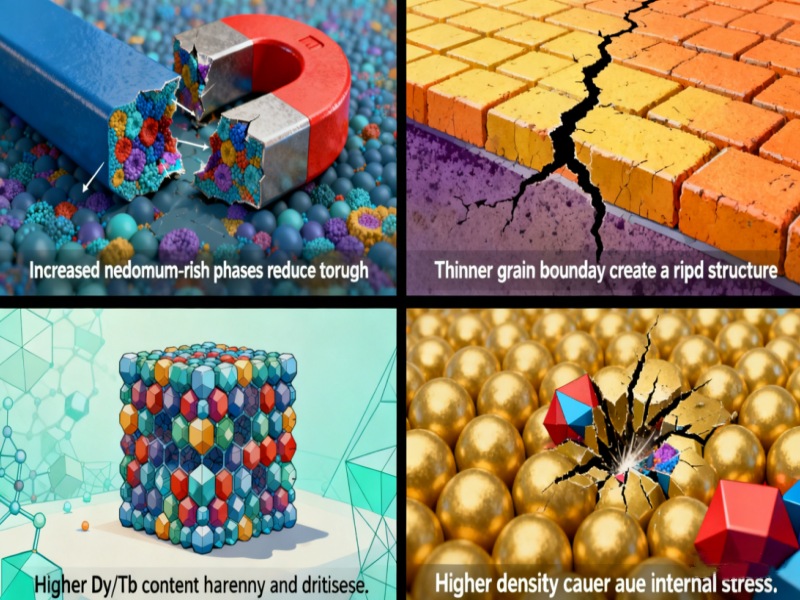
The insufficient mechanical strength of high grade ndfeb magnets can be explained by the following four key scientific factors:
Neodymium-rich phases contribute to magnetic domain orientation, but they are inherently brittle.
High-purity magnets require more of this phase, which reduces the magnet's ability to absorb mechanical stress.
Thin, well-oriented grain boundaries can provide better magnetic properties, but they also provide pathways for rapid crack propagation when the magnet is subjected to impact.
These rare earth elements can improve high-temperature stability, but they also harden the grain structure, making the material more prone to fracture.
When grains are more tightly packed, the material's microscopic flexibility decreases.
Any external impact will propagate rapidly through the structure, leading to breakage or cracking.
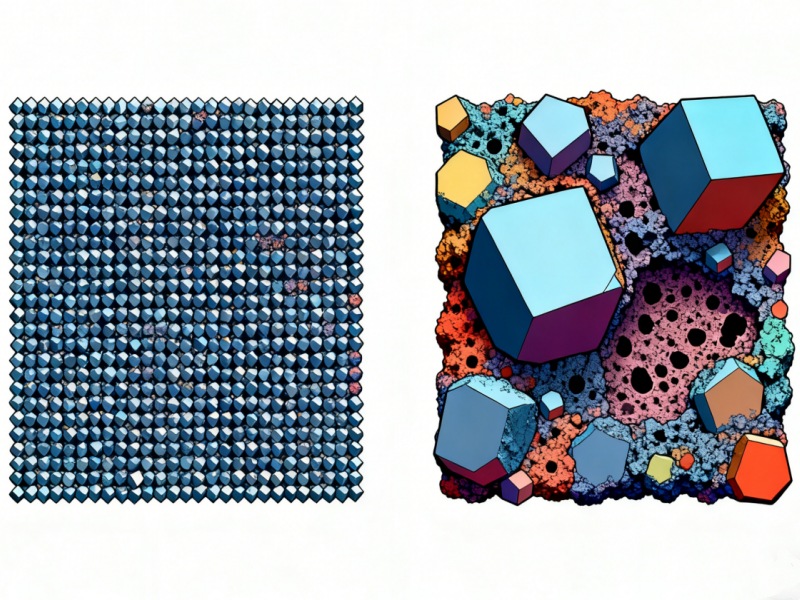
Why do lower-grade magnets feel "stronger"?
Lower-grade magnets typically have:
These characteristics make them mechanically stronger, even if they produce less magnetic force.
Conclusion
High grade magnets inevitably involve a trade-off: stronger magnetic force, but reduced mechanical toughness. The fine microstructure of N50 or N52 grade neo magnets also makes them more susceptible to fracture. Understanding this principle helps engineers and purchasing personnel select the appropriate magnet grade and properly handle high-performance magnets.
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on