 Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
What Are You Looking For?
Compared to a bare magnet of the same size, a pot magnet with steel shell can increase its effective pulling force by two to five times. However, many people don't realize that the shell shape is crucial to magnetic field distribution. Different shell geometries affect not only the strength of the attractive force but also the distribution of the magnetic field across the contact surface.
Basic Principles of Pot Magnets
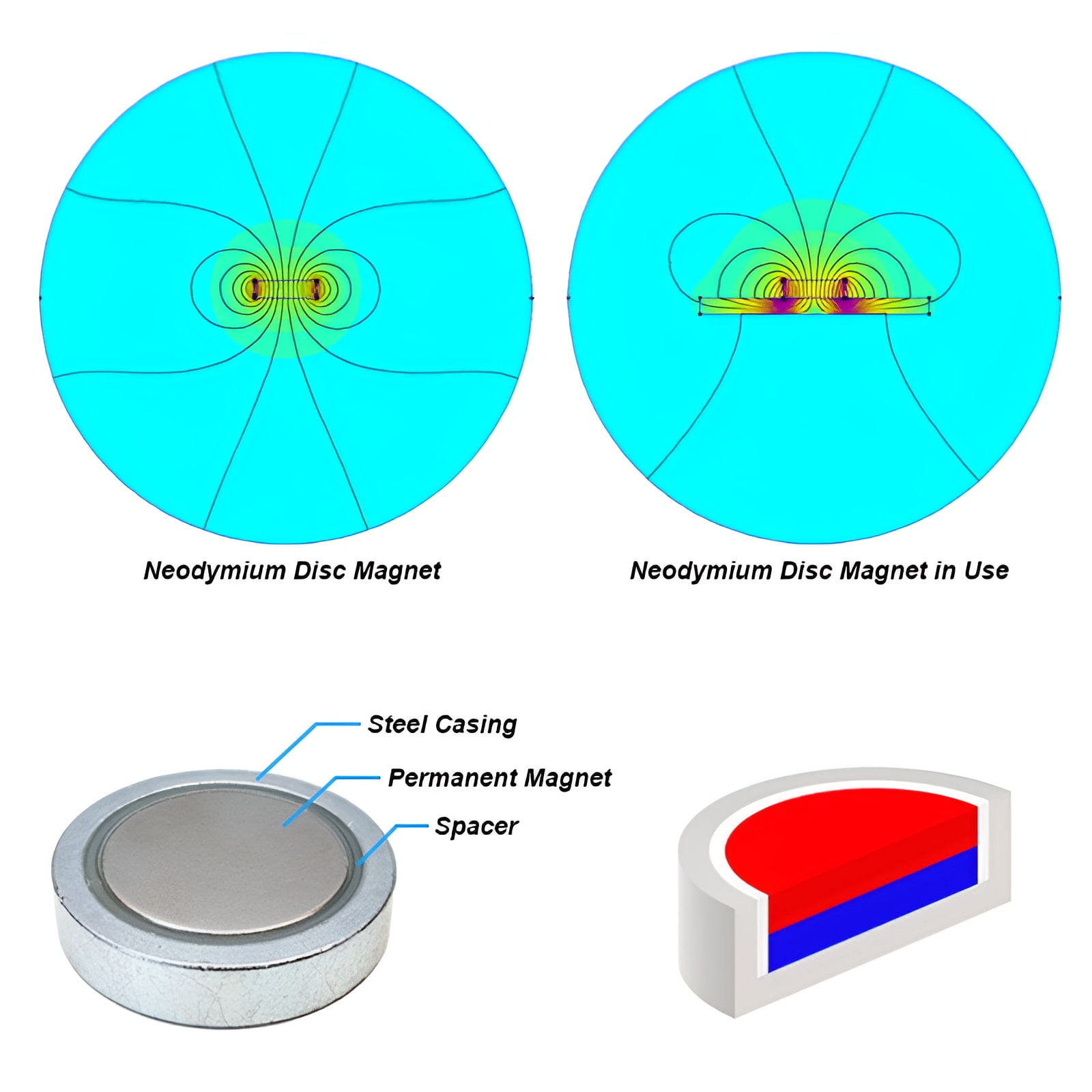
Pot magnets typically consist of three main components:
The shell acts like a magnetic conductor. Instead of allowing magnetic flux to escape in all directions, it guides the flux along a specific path, concentrating it on the open pole surface. This design improves efficiency and protects the magnet from breakage or corrosion.
Comparison of Different Shell Shapes
1. Round Shell Housing Pot magnets
2. Shallow-Walled or Flat-Walled Housing Pot Magnets
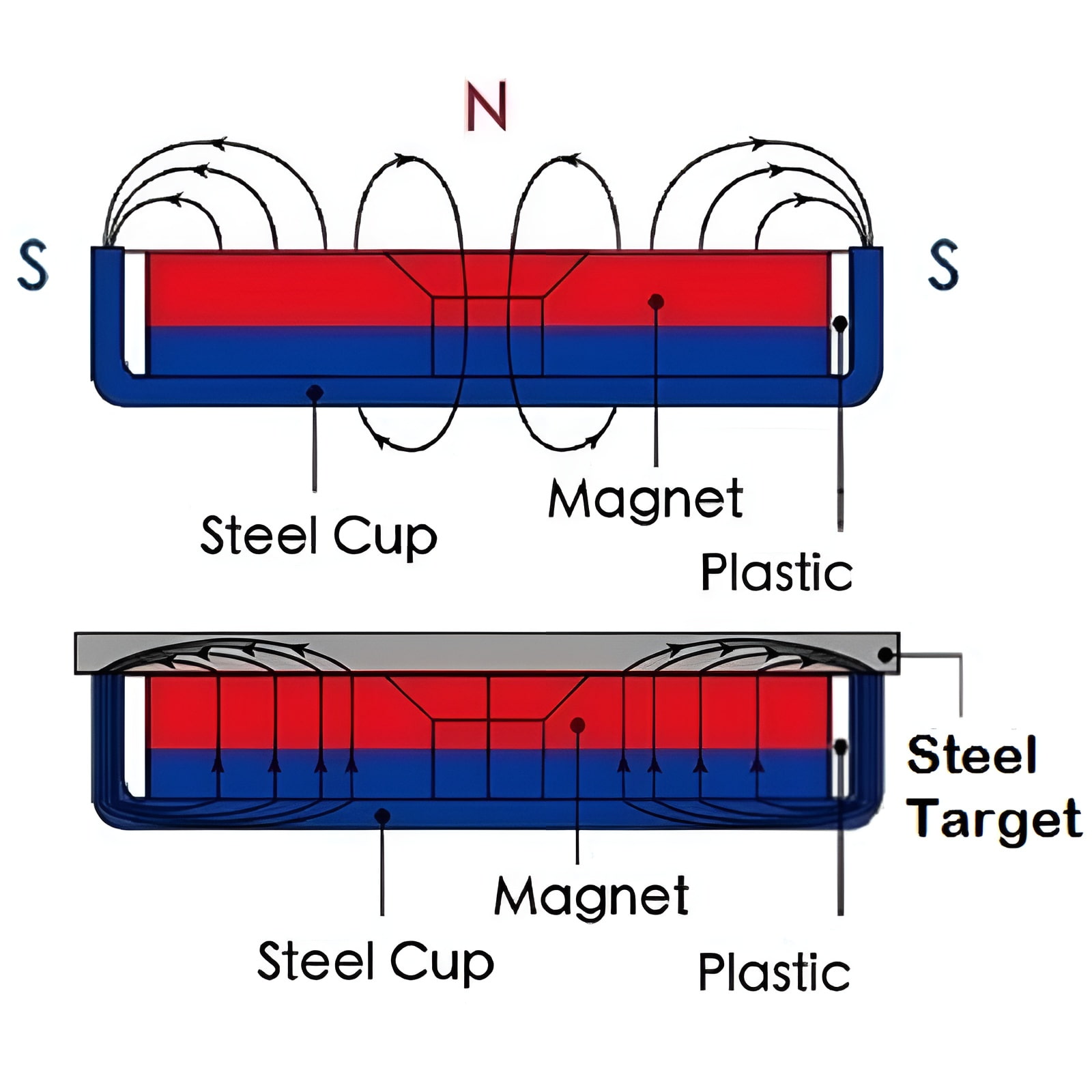
3. Square or Rectangular Housing Pot Magnets
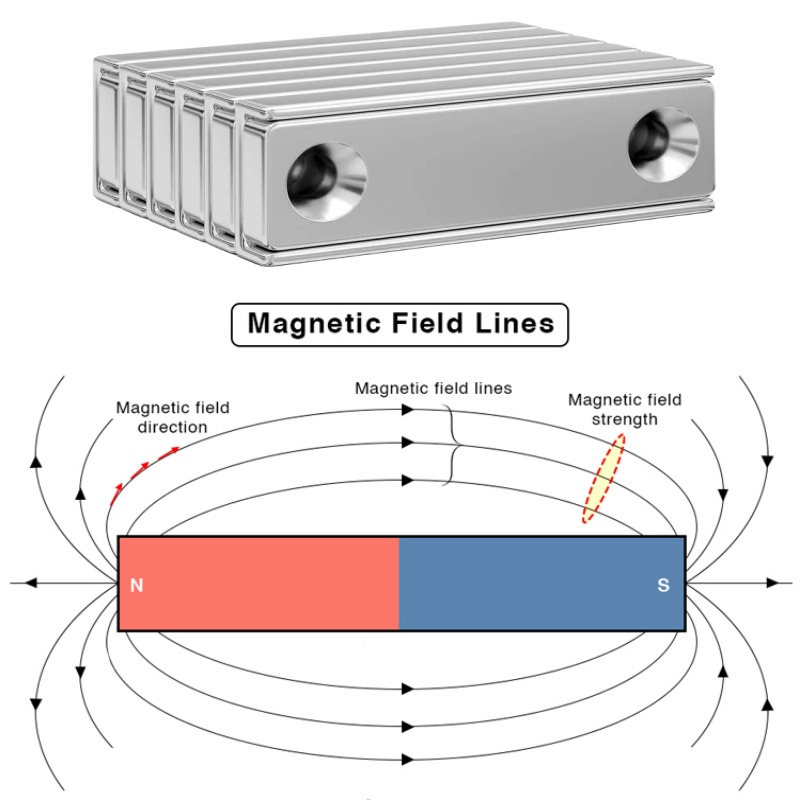
Why Housing Shape Matters
The design of the steel housing affects magnetic circuit efficiency. A deeper housing increases pull force but limits the working distance. A shallower housing extends the magnetic field over a larger area but reduces maximum holding force. Engineers often need to balance pull force, reach, and application environment when selecting the appropriate pot magnet design.
Pot magnets may appear simple, but their performance depends heavily on the geometry of the housing. From round housings that maximize vertical force to flat, square housings that optimize reach and alignment, each design has its own unique applications. By understanding these magnetic circuit principles, neodymium pot magnets suppliers and engineers can provide better choices for industrial, commercial, and domestic applications.
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on