 Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
What Are You Looking For?
Neodymium iron boron (NdFeB) magnets are widely recognized for their exceptional magnetic properties, including high remanence (Br), coercivity (Hc), and maximum energy product (BHmax). These characteristics are not solely dictated by chemical composition but are also profoundly influenced by micro structure. A deeper understanding of the micro structural factors affecting magnetic performance is crucial for optimizing these magnets in high-tech applications such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, and advanced electronics.
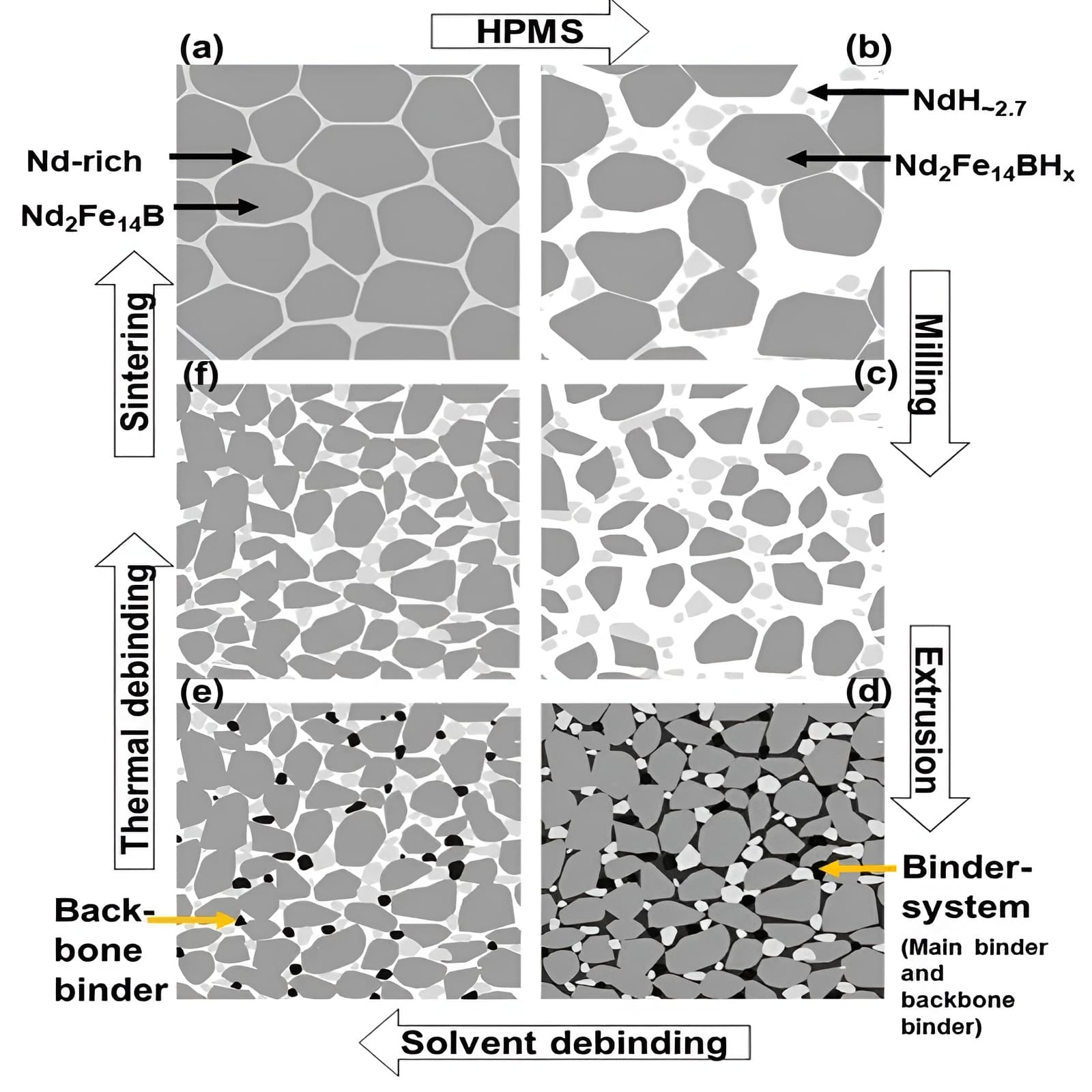
The micro structure of NdFeB magnets consists of several essential phases that determine their performance:
The grain size and distribution of these phases play a critical role in determining the magnet’s final properties. Smaller and well-distributed grains enhance coercivity by preventing domain wall movement, leading to improved performance.
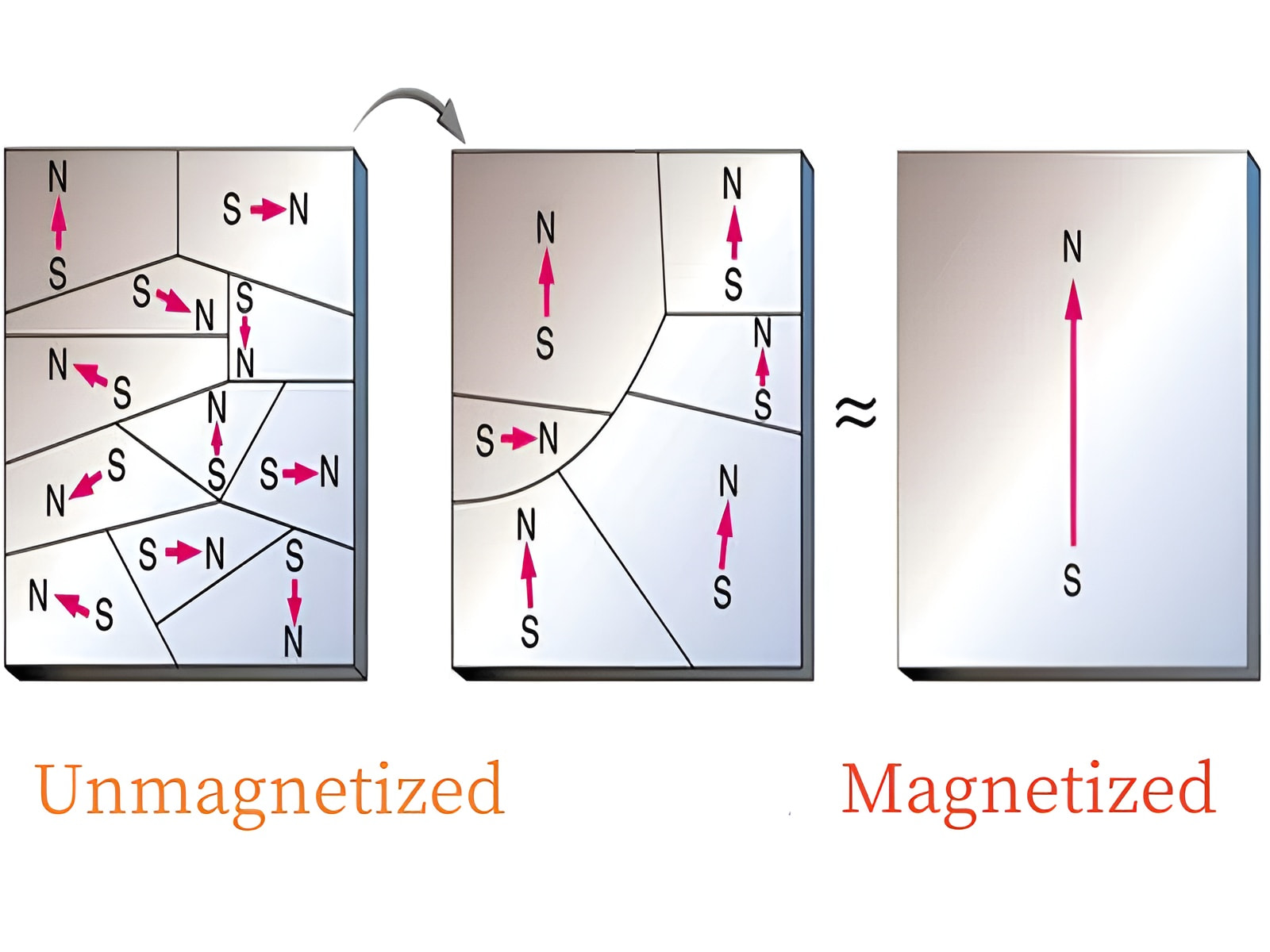
Magnetic domains are microscopic regions within a material where atomic moments are aligned. The structure of these domains directly influences key magnetic parameters:
By controlling domain structure, engineers can fine-tune the balance between remanence and coercivity, optimizing NdFeB permanent magnets for specific applications.
Various techniques are employed to refine the micro structure of NdFeB magnets, leading to enhanced magnetic properties:
The micro structure of strong neodymium NdFeB magnets plays a fundamental role in determining their magnetic properties. By leveraging advanced processing techniques and material innovations, researchers can develop magnets with superior coercivity, remanence, and stability, paving the way for advancements in various high-tech industries.
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on