Choosing the right neodymium magnet is not just about picking the strongest option available—it’s about selecting the most suitable magnet based on the unique requirements of your application. Whether you're designing precision electronic components, enhancing packaging functionality, or building high-efficiency motors, selecting the correct grade, shape, coating, and magnetization direction is crucial for performance, safety, and cost-efficiency.
Packaging: Small Size, Strong Hold, and Aesthetics
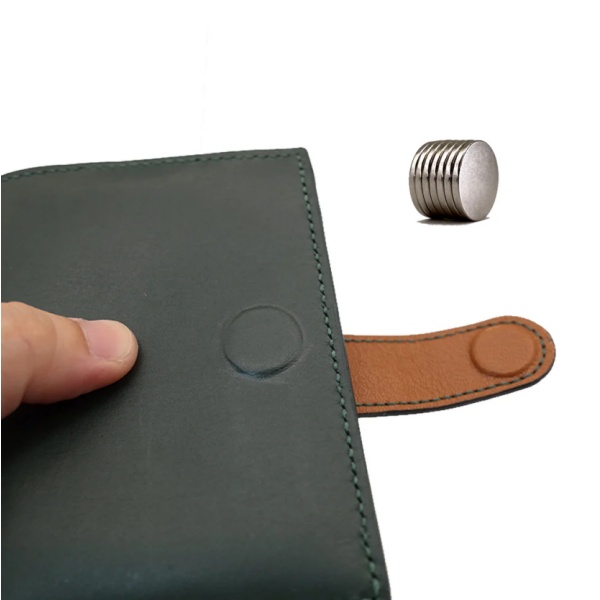

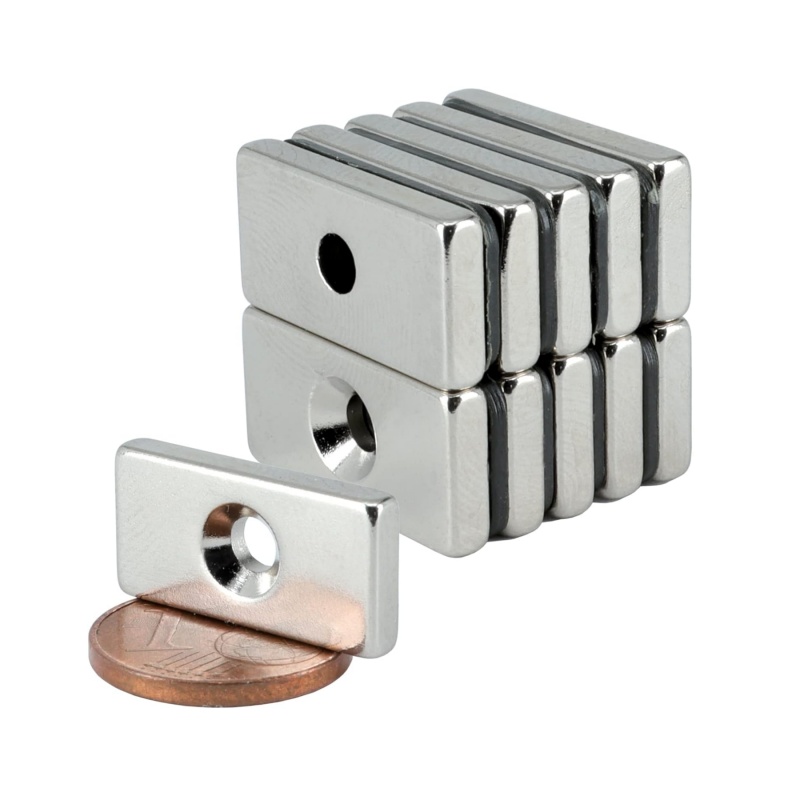
In the packaging industry—especially in luxury goods or reusable closures—neodymium magnets must be small yet powerful. Disc or block neodymium magnets with diameters as small as 5mm are commonly used to ensure discreet placement while maintaining a secure seal. Grades like N35 or N38 are usually sufficient, as excessive strength could make the packaging hard to open or damage the product.
Surface treatment also matters. Nickel, black epoxy, or even gold-plated magnets may be chosen for aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. If the magnet will be enclosed in cardboard or fabric, the magnetization direction must be axial to allow for reliable vertical pull.
Electronics: Precision, Stability, and Miniaturization
In electronics, magnets are found in speakers, sensors, vibration motors, and wireless charging devices. Here, both size and magnetic precision are critical. High-grade magnets such as N52 or N48M are favored due to their strong magnetic field in small volumes. Tight dimensional tolerances and consistency in magnetization are essential to avoid functional discrepancies in mass-produced devices.
Coating is especially important for electronics—magnets must resist corrosion from moisture or heat. Thin epoxy coatings or triple-layered NiCuNi coatings permanent magnets are common choices. Furthermore, magnetization direction may vary based on the sensor design (e.g., radial for rotary encoders).
Motors: High Power, Heat Resistance, and Durability
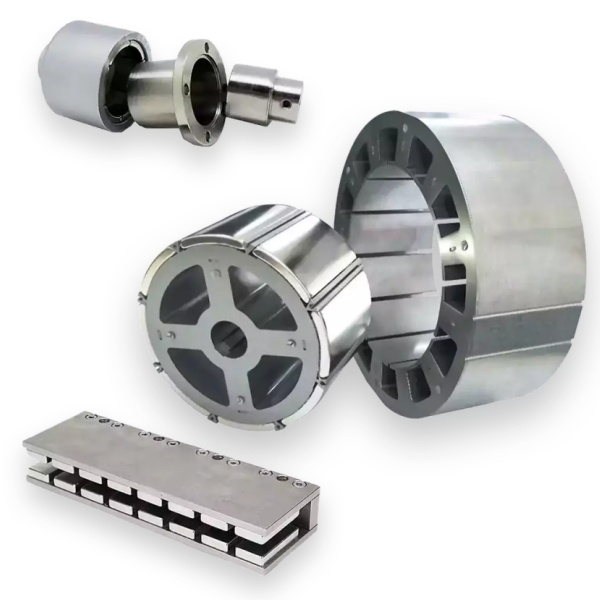

When it comes to motors—whether in drones, e-bikes, or automotive EVs—neodymium magnets play a central role in determining performance and energy efficiency. For these applications, high-grade and high-temperature-resistant magnets such as N42SH, N48H, or even N35EH are necessary to withstand the heat generated by continuous operation.
Curved sintered neodymium magnets are commonly used in stator and rotor assemblies. Coatings like phosphate or epoxy offer improved insulation and durability. Engineers must also consider magnetic orientation, matching the motor design for optimal torque and rotational speed.
Conclusion
Choosing the right neodymium magnet starts with a deep understanding of the application scenario. If you're unsure which specification best fits your project, our team offers tailored consulting services to help you make an informed decision. Contact us today to explore our full range of neodymium magnet solutions for packaging, electronics, and motor systems.






 en
en de
de Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.
Hefei Super Electronics Co., Ltd.









 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
